Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts
Moral Psychology Drives Environmental Concern
The story so far ...
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4
‘we hypothesized that liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms’
Feinberg & Willer, 2013 p. 2
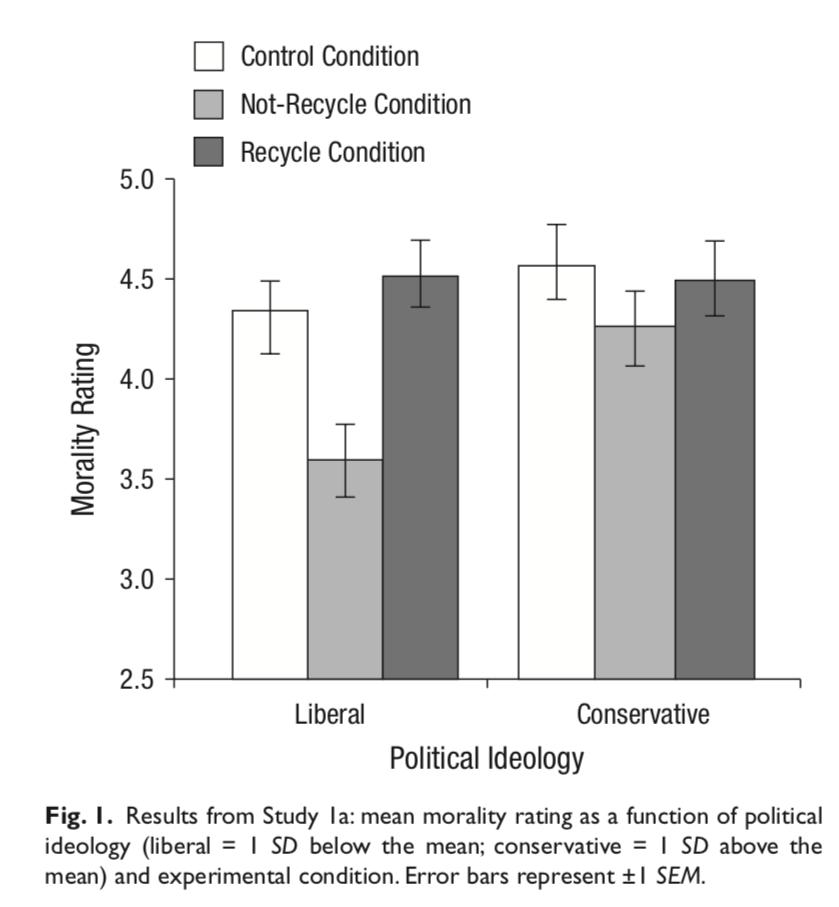
Feinberg & Willer, 2013 figure 1
4
‘we hypothesized that liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms’
Feinberg & Willer, 2013 p. 2
‘A mediation analysis (Preacher & Hayes, 2008) revealed that perception of the environment as a moral issue was a significant partial mediator of the relationship between liberalism and environmental attitudes’ (Feinberg & Willer, 2013, p. 3).
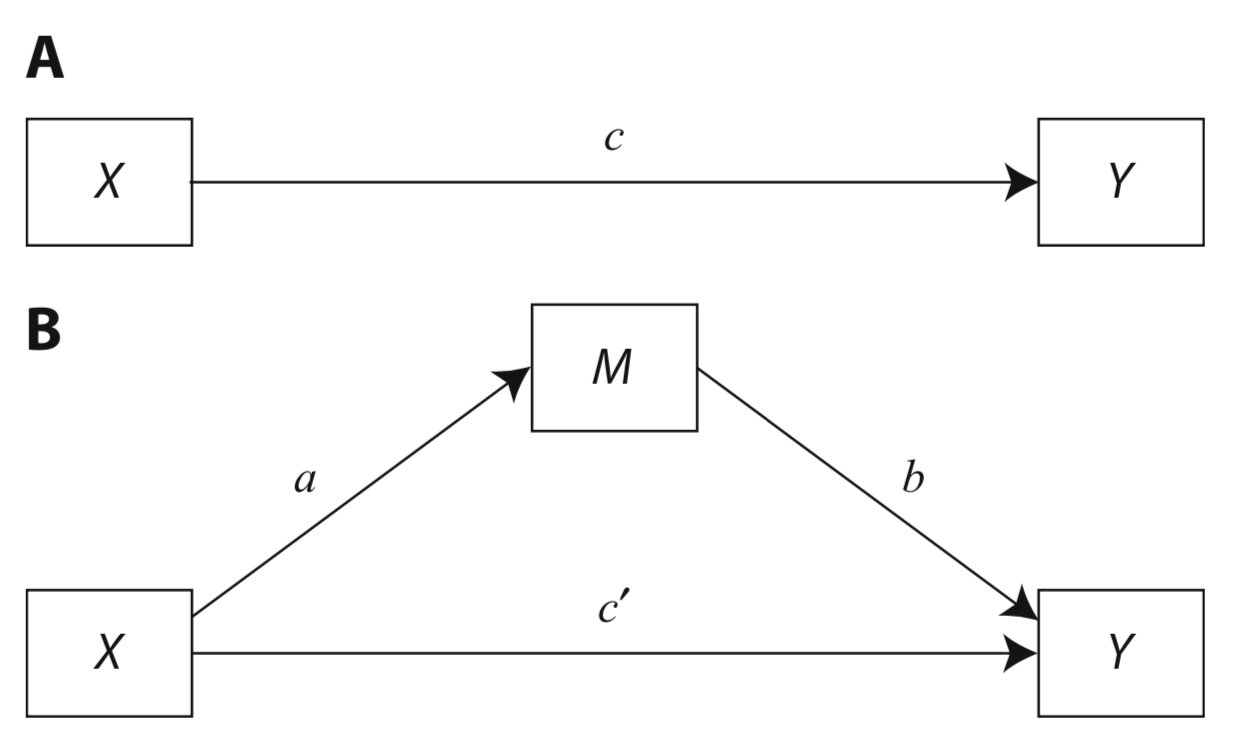
Preacher & Hayes (2008, p. figure 1)
4
‘we hypothesized that liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms’
Feinberg & Willer, 2013 p. 2
Do cultural differences in moral psychology explain political conflict on climate change? Yes!
Plan:
Work through Feinberg & Willer, 2013 ‘The Moral Roots of Environmental Attitudes’